How to Run Database Initializer Again
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Tutorial: Get started with EF Core in an ASP.Cyberspace MVC web app
Past Tom Dykstra and Rick Anderson
This tutorial teaches ASP.Internet Core MVC and Entity Framework Core with controllers and views. Razor Pages is an alternative programming model. For new development, we recommend Razor Pages over MVC with controllers and views. See the Razor Pages version of this tutorial. Each tutorial covers some material the other doesn't:
Some things this MVC tutorial has that the Razor Pages tutorial doesn't:
- Implement inheritance in the data model
- Perform raw SQL queries
- Use dynamic LINQ to simplify lawmaking
Some things the Razor Pages tutorial has that this one doesn't:
- Use Select method to load related data
- All-time practices for EF.
This tutorial has not been updated for ASP.NET Core vi. The ASP.NET Core half dozen web templates utilise the new minimal hosting model, which unifies Startup.cs and Plan.cs into a single Program.cs file. Until this tutorial is updated, see Razor Pages with Entity Framework Core in ASP.Internet Core - Tutorial 1 of viii and Part 4, add a model to an ASP.NET Core MVC app on how to use EF with the new minimal hosting model. Updating the tutorial for ASP.NET Core 6 is tracked in this GitHub issue.
The Contoso University sample spider web app demonstrates how to create an ASP.Net Core MVC spider web app using Entity Framework (EF) Core and Visual Studio.
The sample app is a spider web site for a fictional Contoso Academy. It includes functionality such equally student admission, course cosmos, and instructor assignments. This is the offset in a serial of tutorials that explain how to build the Contoso University sample app.
Prerequisites
- If yous're new to ASP.NET Core MVC, become through the Go started with ASP.Internet Cadre MVC tutorial series before starting this ane.
- Visual Studio 2019 16.8 or afterward with the ASP.NET and spider web development workload
- .Internet five.0 SDK
Database engines
The Visual Studio instructions employ SQL Server LocalDB, a version of SQL Server Express that runs only on Windows.
Solve problems and troubleshoot
If y'all run into a problem you can't resolve, you can generally find the solution by comparing your code to the completed project. For a list of mutual errors and how to solve them, run across the Troubleshooting section of the last tutorial in the serial. If you lot don't find what you need in that location, you tin postal service a question to StackOverflow.com for ASP.Net Core or EF Core.
Tip
This is a series of 10 tutorials, each of which builds on what is done in earlier tutorials. Consider saving a copy of the project afterward each successful tutorial completion. Then if y'all run into problems, you lot can start over from the previous tutorial instead of going back to the beginning of the whole series.
Contoso University web app
The app congenital in these tutorials is a bones university web site.
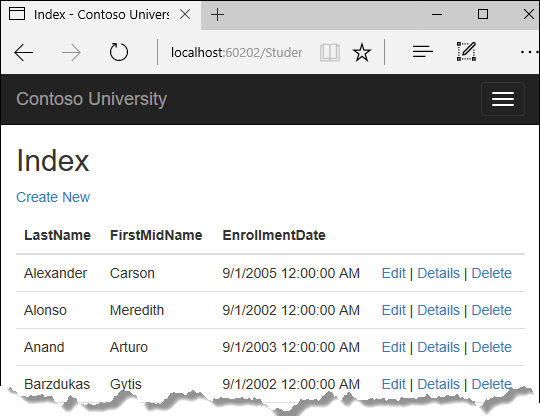
Users tin can view and update student, course, and instructor information. Here are a few of the screens in the app:

Create web app
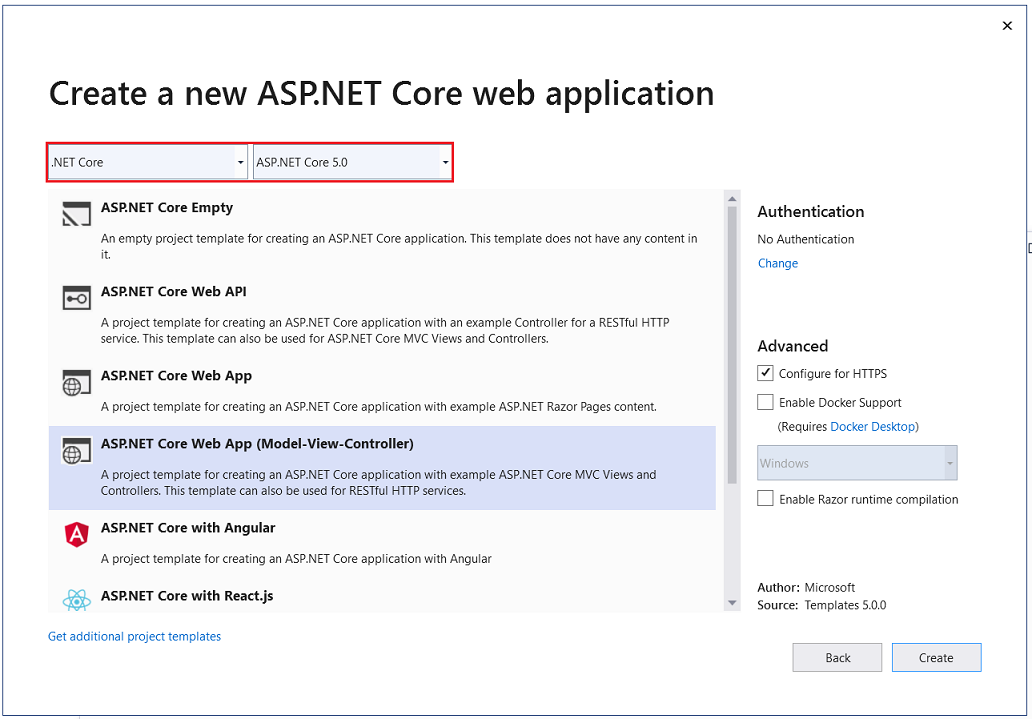
- Showtime Visual Studio and select Create a new project.
- In the Create a new project dialog, select ASP.NET Core Web Application > Adjacent.
- In the Configure your new project dialog, enter
ContosoUniversityfor Project name. It'southward of import to use this exact name including capitalization, so eachnamespacematches when lawmaking is copied. - Select Create.
- In the Create a new ASP.Cyberspace Cadre spider web awarding dialog, select:
- .NET Core and ASP.NET Core 5.0 in the dropdowns.
- ASP.Net Core Web App (Model-View-Controller).
- Create
Gear up the site manner
A few basic changes set up the site carte du jour, layout, and home page.
Open Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml and make the following changes:
- Modify each occurrence of
ContosoUniversitytoContoso University. In that location are three occurrences. - Add menu entries for About, Students, Courses, Instructors, and Departments, and delete the Privacy card entry.
The preceding changes are highlighted in the following lawmaking:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-viii" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=ane.0" /> <championship>@ViewData["Title"] - Contoso University</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" /> <link rel="stylesheet" href="~/css/site.css" /> </head> <body> <header> <nav class="navbar navbar-expand-sm navbar-toggleable-sm navbar-low-cal bg-white border-bottom box-shadow mb-three"> <div form="container"> <a class="navbar-brand" asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Index">Contoso University</a> <push class="navbar-toggler" blazon="button" data-toggle="plummet" data-target=".navbar-collapse" aria-controls="navbarSupportedContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-characterization="Toggle navigation"> <span course="navbar-toggler-icon"></span> </button> <div class="navbar-plummet plummet d-sm-inline-flex justify-content-between"> <ul class="navbar-nav flex-grow-1"> <li class="nav-item"> <a class="nav-link text-dark" asp-expanse="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Index">Dwelling house</a> </li> <li class="nav-item"> <a class="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Most">Virtually</a> </li> <li class="nav-item"> <a class="nav-link text-dark" asp-expanse="" asp-controller="Students" asp-action="Index">Students</a> </li> <li class="nav-particular"> <a class="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Courses" asp-action="Index">Courses</a> </li> <li form="nav-item"> <a grade="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Instructors" asp-activeness="Index">Instructors</a> </li> <li class="nav-item"> <a class="nav-link text-nighttime" asp-expanse="" asp-controller="Departments" asp-activeness="Index">Departments</a> </li> </ul> </div> </div> </nav> </header> <div class="container"> <main part="main" class="atomic number 82-3"> @RenderBody() </main> </div> <footer form="border-top footer text-muted"> <div class="container"> © 2020 - Contoso University - <a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Privacy">Privacy</a> </div> </footer> <script src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js"></script> <script src="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script> <script src="~/js/site.js" asp-append-version="truthful"></script> @await RenderSectionAsync("Scripts", required: false) </trunk> </html> In Views/Dwelling house/Index.cshtml, replace the contents of the file with the following markup:
@{ ViewData["Championship"] = "Home Page"; } <div class="jumbotron"> <h1>Contoso University</h1> </div> <div class="row"> <div class="col-doctor-4"> <h2>Welcome to Contoso Academy</h2> <p> Contoso University is a sample application that demonstrates how to utilise Entity Framework Cadre in an ASP.NET Core MVC spider web application. </p> </div> <div class="col-md-4"> <h2>Build it from scratch</h2> <p>Y'all tin build the application by following the steps in a serial of tutorials.</p> <p><a class="btn btn-default" href="https://docs.asp.net/en/latest/information/ef-mvc/intro.html">See the tutorial »</a></p> </div> <div class="col-doc-4"> <h2>Download it</h2> <p>You tin can download the completed project from GitHub.</p> <p><a form="btn btn-default" href="https://github.com/dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs/tree/main/aspnetcore/data/ef-mvc/intro/samples/5cu-last">Come across project source lawmaking »</a></p> </div> </div> Press CTRL+F5 to run the project or choose Debug > Start Without Debugging from the card. The home page is displayed with tabs for the pages created in this tutorial.
EF Core NuGet packages
This tutorial uses SQL Server, and the provider bundle is Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.
The EF SQL Server package and its dependencies, Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore and Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Relational, provide runtime back up for EF.
Add the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.EntityFrameworkCore NuGet packet. In the Parcel Director Console (PMC), enter the following commands to add together the NuGet packages:
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.EntityFrameworkCore Install-Packet Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer The Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.EntityFrameworkCore NuGet package provides ASP.Internet Core middleware for EF Core error pages. This middleware helps to detect and diagnose errors with EF Core migrations.
For data near other database providers that are available for EF Core, see Database providers.
Create the data model
The following entity classes are created for this app:
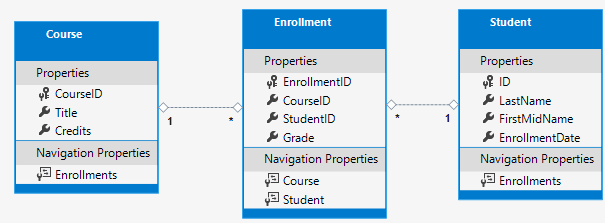
The preceding entities have the post-obit relationships:
- A i-to-many relationship betwixt
StudentandEnrollmententities. A student can be enrolled in any number of courses. - A ane-to-many relationship between
FormandEnrollmententities. A course tin have any number of students enrolled in information technology.
In the post-obit sections, a class is created for each of these entities.
The Student entity

In the Models folder, create the Pupil class with the following lawmaking:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; namespace ContosoUniversity.Models { public course Student { public int ID { get; set; } public string LastName { become; ready; } public string FirstMidName { get; gear up; } public DateTime EnrollmentDate { go; set up; } public ICollection<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } } } The ID property is the primary key (PK) column of the database table that corresponds to this class. Past default, EF interprets a property that's named ID or classnameID every bit the chief key. For example, the PK could be named StudentID rather than ID.
The Enrollments property is a navigation property. Navigation properties concur other entities that are related to this entity. The Enrollments property of a Pupil entity:
- Contains all of the
Enrollmententities that are related to thatStudententity. - If a specific
Studentrow in the database has two relatedEnrollmentrows:- That
Studententity'sEnrollmentsnavigation belongings contains those 2Enrollmententities.
- That
Enrollment rows contain a educatee'south PK value in the StudentID strange central (FK) column.
If a navigation property can hold multiple entities:
- The type must be a listing, such equally
ICollection<T>,List<T>, orHashSet<T>. - Entities can be added, deleted, and updated.
Many-to-many and one-to-many navigation relationships can contain multiple entities. When ICollection<T> is used, EF creates a HashSet<T> collection by default.
The Enrollment entity

In the Models folder, create the Enrollment class with the following code:
namespace ContosoUniversity.Models { public enum Course { A, B, C, D, F } public class Enrollment { public int EnrollmentID { become; prepare; } public int CourseID { get; set; } public int StudentID { get; gear up; } public Grade? Grade { get; set; } public Course Form { get; ready; } public Student Student { become; ready; } } } The EnrollmentID property is the PK. This entity uses the classnameID pattern instead of ID past itself. The Pupil entity used the ID pattern. Some developers prefer to use one pattern throughout the data model. In this tutorial, the variation illustrates that either blueprint can be used. A afterward tutorial shows how using ID without classname makes information technology easier to implement inheritance in the data model.
The Grade property is an enum. The ? after the Form blazon annunciation indicates that the Grade property is nullable. A grade that's nix is unlike from a zero grade. null means a form isn't known or hasn't been assigned even so.
The StudentID holding is a strange key (FK), and the corresponding navigation property is Student. An Enrollment entity is associated with one Student entity, so the property can simply hold a single Pupil entity. This differs from the Student.Enrollments navigation property, which tin agree multiple Enrollment entities.
The CourseID property is a FK, and the respective navigation property is Course. An Enrollment entity is associated with one Grade entity.
Entity Framework interprets a property as a FK holding if it's named <navigation property name><primary primal property name>. For example, StudentID for the Student navigation property since the Student entity's PK is ID. FK backdrop can likewise be named <primary key property proper name>. For case, CourseID considering the Course entity's PK is CourseID.
The Course entity

In the Models folder, create the Course class with the following code:
using System.Collections.Generic; using Organisation.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; namespace ContosoUniversity.Models { public course Class { [DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.None)] public int CourseID { get; set; } public string Title { get; set; } public int Credits { get; set; } public ICollection<Enrollment> Enrollments { go; set; } } } The Enrollments property is a navigation property. A Course entity can be related to any number of Enrollment entities.
The DatabaseGenerated aspect is explained in a subsequently tutorial. This attribute allows inbound the PK for the class rather than having the database generate information technology.
Create the database context
The primary class that coordinates EF functionality for a given data model is the DbContext database context class. This class is created by deriving from the Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContext form. The DbContext derived class specifies which entities are included in the data model. Some EF behaviors can exist customized. In this project, the class is named SchoolContext.
In the project folder, create a folder named Data.
In the Information folder create a SchoolContext form with the following code:
using ContosoUniversity.Models; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; namespace ContosoUniversity.Data { public class SchoolContext : DbContext { public SchoolContext(DbContextOptions<SchoolContext> options) : base(options) { } public DbSet<Course> Courses { get; gear up; } public DbSet<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } public DbSet<Student> Students { become; prepare; } } } The preceding lawmaking creates a DbSet belongings for each entity set. In EF terminology:
- An entity set typically corresponds to a database table.
- An entity corresponds to a row in the tabular array.
The DbSet<Enrollment> and DbSet<Course> statements could be omitted and information technology would work the same. EF would include them implicitly because:
- The
Studententity references theEnrollmententity. - The
Enrollmententity references theGradeentity.
When the database is created, EF creates tables that have names the aforementioned every bit the DbSet holding names. Holding names for collections are typically plural. For example, Students rather than Student. Developers disagree virtually whether table names should be pluralized or not. For these tutorials, the default behavior is overridden by specifying atypical table names in the DbContext. To practise that, add the following highlighted code after the terminal DbSet property.
using ContosoUniversity.Models; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; namespace ContosoUniversity.Data { public class SchoolContext : DbContext { public SchoolContext(DbContextOptions<SchoolContext> options) : base(options) { } public DbSet<Course> Courses { get; set; } public DbSet<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Course>().ToTable("Course"); modelBuilder.Entity<Enrollment>().ToTable("Enrollment"); modelBuilder.Entity<Student>().ToTable("Student"); } } } Register the SchoolContext
ASP.Cyberspace Core includes dependency injection. Services, such as the EF database context, are registered with dependency injection during app startup. Components that require these services, such as MVC controllers, are provided these services via constructor parameters. The controller constructor code that gets a context instance is shown after in this tutorial.
To register SchoolContext every bit a service, open Startup.cs, and add the highlighted lines to the ConfigureServices method.
using ContosoUniversity.Data; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Architect; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting; namespace ContosoUniversity { public course Startup { public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) { Configuration = configuration; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddDbContext<SchoolContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"))); services.AddControllersWithViews(); } The name of the connection string is passed in to the context past calling a method on a DbContextOptionsBuilder object. For local evolution, the ASP.Net Core configuration organization reads the connection cord from the appsettings.json file.
Open the appsettings.json file and add together a connection cord as shown in the following markup:
{ "ConnectionStrings": { "DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=ContosoUniversity1;Trusted_Connection=Truthful;MultipleActiveResultSets=true" }, "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Data", "Microsoft": "Alert", "Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*" } Add the database exception filter
Add AddDatabaseDeveloperPageExceptionFilter to ConfigureServices as shown in the post-obit code:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddDbContext<SchoolContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"))); services.AddDatabaseDeveloperPageExceptionFilter(); services.AddControllersWithViews(); } The AddDatabaseDeveloperPageExceptionFilter provides helpful error information in the evolution surroundings.
SQL Server Express LocalDB
The connexion string specifies SQL Server LocalDB. LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express Database Engine and is intended for app development, non production employ. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there's no complex configuration. Past default, LocalDB creates .mdf DB files in the C:/Users/<user> directory.
Initialize DB with examination information
EF creates an empty database. In this section, a method is added that'southward called after the database is created in social club to populate it with test data.
The EnsureCreated method is used to automatically create the database. In a after tutorial, you see how to handle model changes by using Lawmaking First Migrations to change the database schema instead of dropping and re-creating the database.
In the Data folder, create a new class named DbInitializer with the following lawmaking:
using ContosoUniversity.Models; using Organization; using System.Linq; namespace ContosoUniversity.Data { public static class DbInitializer { public static void Initialize(SchoolContext context) { context.Database.EnsureCreated(); // Look for any students. if (context.Students.Any()) { return; // DB has been seeded } var students = new Pupil[] { new Student{FirstMidName="Carson",LastName="Alexander",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2005-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Meredith",LastName="Alonso",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Arturo",LastName="Anand",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2003-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Gytis",LastName="Barzdukas",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Yan",LastName="Li",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Peggy",LastName="Justice",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2001-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Laura",LastName="Norman",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2003-09-01")}, new Educatee{FirstMidName="Nino",LastName="Olivetto",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2005-09-01")} }; foreach (Student s in students) { context.Students.Add(south); } context.SaveChanges(); var courses = new Class[] { new Course{CourseID=1050,Title="Chemical science",Credits=3}, new Course{CourseID=4022,Title="Microeconomics",Credits=3}, new Class{CourseID=4041,Title="Macroeconomics",Credits=3}, new Course{CourseID=1045,Championship="Calculus",Credits=4}, new Course{CourseID=3141,Title="Trigonometry",Credits=4}, new Grade{CourseID=2021,Title="Composition",Credits=3}, new Course{CourseID=2042,Title="Literature",Credits=4} }; foreach (Grade c in courses) { context.Courses.Add together(c); } context.SaveChanges(); var enrollments = new Enrollment[] { new Enrollment{StudentID=1,CourseID=1050,Class=Grade.A}, new Enrollment{StudentID=1,CourseID=4022,Course=Grade.C}, new Enrollment{StudentID=1,CourseID=4041,Grade=Grade.B}, new Enrollment{StudentID=two,CourseID=1045,Grade=Grade.B}, new Enrollment{StudentID=ii,CourseID=3141,Class=Form.F}, new Enrollment{StudentID=2,CourseID=2021,Course=Grade.F}, new Enrollment{StudentID=3,CourseID=1050}, new Enrollment{StudentID=4,CourseID=1050}, new Enrollment{StudentID=4,CourseID=4022,Grade=Form.F}, new Enrollment{StudentID=five,CourseID=4041,Grade=Grade.C}, new Enrollment{StudentID=6,CourseID=1045}, new Enrollment{StudentID=7,CourseID=3141,Grade=Course.A}, }; foreach (Enrollment east in enrollments) { context.Enrollments.Add(e); } context.SaveChanges(); } } } The preceding code checks if the database exists:
- If the database is not found;
- It is created and loaded with exam data. It loads test data into arrays rather than
Listing<T>collections to optimize functioning.
- It is created and loaded with exam data. It loads test data into arrays rather than
- If the database is establish, it takes no action.
Update Plan.cs with the following code:
using ContosoUniversity.Data; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using System; namespace ContosoUniversity { public grade Programme { public static void Chief(cord[] args) { var host = CreateHostBuilder(args).Build(); CreateDbIfNotExists(host); host.Run(); } private static void CreateDbIfNotExists(IHost host) { using (var scope = host.Services.CreateScope()) { var services = scope.ServiceProvider; effort { var context = services.GetRequiredService<SchoolContext>(); DbInitializer.Initialize(context); } catch (Exception ex) { var logger = services.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Program>>(); logger.LogError(ex, "An fault occurred creating the DB."); } } } public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) => Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) .ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder => { webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>(); }); } } Program.cs does the following on app startup:
- Get a database context instance from the dependency injection container.
- Telephone call the
DbInitializer.Initializemethod. - Dispose the context when the
Initializemethod completes equally shown in the post-obit lawmaking:
public static void Primary(string[] args) { var host = CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build(); using (var scope = host.Services.CreateScope()) { var services = telescopic.ServiceProvider; endeavor { var context = services.GetRequiredService<SchoolContext>(); DbInitializer.Initialize(context); } catch (Exception ex) { var logger = services.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Program>>(); logger.LogError(ex, "An fault occurred while seeding the database."); } } host.Run(); } The first time the app is run, the database is created and loaded with test data. Whenever the data model changes:
- Delete the database.
- Update the seed method, and start afresh with a new database.
In later tutorials, the database is modified when the data model changes, without deleting and re-creating it. No data is lost when the data model changes.
Create controller and views
Employ the scaffolding engine in Visual Studio to add an MVC controller and views that will use EF to query and salvage information.
The automatic creation of CRUD activity methods and views is known as scaffolding.
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the
Controllersfolder and select Add > New Scaffolded Item. - In the Add Scaffold dialog box:
- Select MVC controller with views, using Entity Framework.
- Click Add. The Add MVC Controller with views, using Entity Framework dialog box appears:
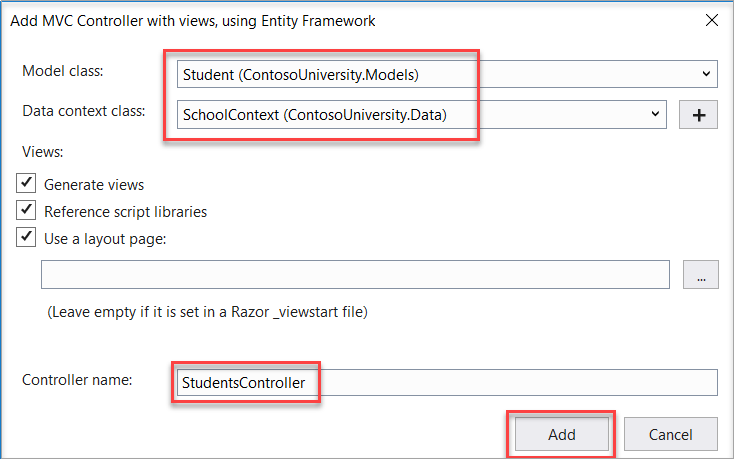
- In Model class, select Student.
- In Data context class, select SchoolContext.
- Accept the default StudentsController as the name.
- Click Add.
The Visual Studio scaffolding engine creates a StudentsController.cs file and a set of views (*.cshtml files) that work with the controller.
Notice the controller takes a SchoolContext as a constructor parameter.
namespace ContosoUniversity.Controllers { public course StudentsController : Controller { private readonly SchoolContext _context; public StudentsController(SchoolContext context) { _context = context; } ASP.Net Core dependency injection takes care of passing an instance of SchoolContext into the controller. You configured that in the Startup class.
The controller contains an Index activeness method, which displays all students in the database. The method gets a list of students from the Students entity set past reading the Students holding of the database context instance:
public async Task<IActionResult> Alphabetize() { return View(wait _context.Students.ToListAsync()); } The asynchronous programming elements in this lawmaking are explained later in the tutorial.
The Views/Students/Index.cshtml view displays this list in a table:
@model IEnumerable<ContosoUniversity.Models.Student> @{ ViewData["Title"] = "Index"; } <h2>Index</h2> <p> <a asp-action="Create">Create New</a> </p> <table class="tabular array"> <thead> <tr> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.LastName) </thursday> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.FirstMidName) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.EnrollmentDate) </thursday> <thursday></th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> @foreach (var item in Model) { <tr> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.LastName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FirstMidName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => particular.EnrollmentDate) </td> <td> <a asp-action="Edit" asp-road-id="@particular.ID">Edit</a> | <a asp-activity="Details" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Details</a> | <a asp-action="Delete" asp-road-id="@item.ID">Delete</a> </td> </tr> } </tbody> </table> Press CTRL+F5 to run the project or cull Debug > Offset Without Debugging from the menu.
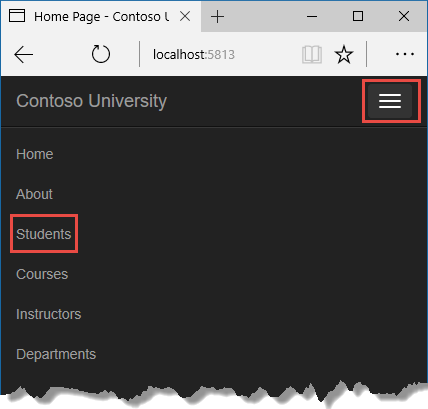
Click the Students tab to see the test data that the DbInitializer.Initialize method inserted. Depending on how narrow your browser window is, you'll run into the Students tab link at the acme of the page or yous'll accept to click the navigation icon in the upper correct corner to run into the link.

View the database
When the app is started, the DbInitializer.Initialize method calls EnsureCreated. EF saw that there was no database:
- So it created a database.
- The
Initializemethod code populated the database with data.
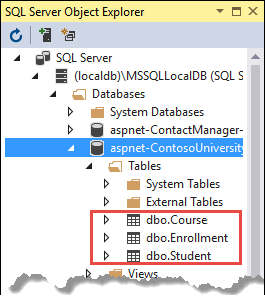
Use SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX) to view the database in Visual Studio:
- Select SQL Server Object Explorer from the View bill of fare in Visual Studio.
- In SSOX, select (localdb)\MSSQLLocalDB > Databases.
- Select
ContosoUniversity1, the entry for the database name that'south in the connection cord in the appsettings.json file. - Aggrandize the Tables node to see the tables in the database.
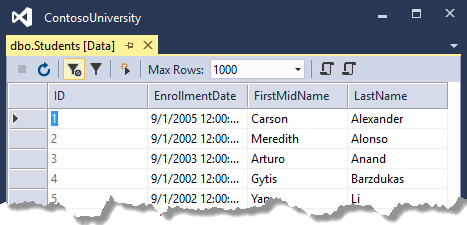
Right-click the Student table and click View Data to encounter the data in the table.
The *.mdf and *.ldf database files are in the C:\Users\<username> folder.
Considering EnsureCreated is chosen in the initializer method that runs on app start, yous could:
- Brand a change to the
Studentgrade. - Delete the database.
- Stop, and then start the app. The database is automatically re-created to friction match the change.
For instance, if an EmailAddress property is added to the Educatee grade, a new EmailAddress column in the re-created tabular array. The view won't display the new EmailAddress property.
Conventions
The corporeality of code written in order for the EF to create a complete database is minimal considering of the use of the conventions EF uses:
- The names of
DbSetbackdrop are used equally table names. For entities not referenced by aDbSetproperty, entity class names are used as table names. - Entity property names are used for column names.
- Entity backdrop that are named
IDorclassnameIDare recognized as PK properties. - A property is interpreted as a FK property if it's named
<navigation holding name><PK holding name>. For example,StudentIDfor theStudentnavigation belongings since theStudententity's PK isID. FK properties can as well be named<chief key property name>. For example,EnrollmentIDsince theEnrollmententity'due south PK isEnrollmentID.
Conventional behavior can be overridden. For instance, table names can exist explicitly specified, as shown earlier in this tutorial. Column names and any property can exist set as a PK or FK.
Asynchronous lawmaking
Asynchronous programming is the default mode for ASP.Cyberspace Core and EF Core.
A web server has a limited number of threads available, and in high load situations all of the available threads might be in use. When that happens, the server can't procedure new requests until the threads are freed upwardly. With synchronous code, many threads may be tied upward while they aren't actually doing any work because they're waiting for I/O to complete. With asynchronous code, when a process is waiting for I/O to complete, its thread is freed upwardly for the server to utilise for processing other requests. Equally a result, asynchronous lawmaking enables server resources to be used more than efficiently, and the server is enabled to handle more traffic without delays.
Asynchronous code does introduce a small amount of overhead at run time, but for depression traffic situations the performance striking is negligible, while for high traffic situations, the potential functioning improvement is substantial.
In the following lawmaking, async, Task<T>, wait, and ToListAsync make the code execute asynchronously.
public async Task<IActionResult> Index() { render View(await _context.Students.ToListAsync()); } - The
asynckeyword tells the compiler to generate callbacks for parts of the method torso and to automatically create theTask<IActionResult>object that's returned. - The return blazon
Task<IActionResult>represents ongoing piece of work with a event of typeIActionResult. - The
awaitkeyword causes the compiler to split up the method into two parts. The kickoff function ends with the performance that's started asynchronously. The second part is put into a callback method that's chosen when the operation completes. -
ToListAsyncis the asynchronous version of theToListextension method.
Some things to be aware of when writing asynchronous code that uses EF:
- But statements that cause queries or commands to exist sent to the database are executed asynchronously. That includes, for example,
ToListAsync,SingleOrDefaultAsync, andSaveChangesAsync. It doesn't include, for example, statements that just modify anIQueryable, such asvar students = context.Students.Where(s => s.LastName == "Davolio"). - An EF context isn't thread safe: don't try to practise multiple operations in parallel. When yous call whatever async EF method, e'er utilise the
awaitkeyword. - To take advantage of the performance benefits of async code, brand sure that whatsoever library packages used also use async if they call any EF methods that cause queries to be sent to the database.
For more information nearly asynchronous programming in .NET, run across Async Overview.
Limit entities fetched
See Operation considerations for information on limiting the number of entities returned from a query.
SQL Logging of Entity Framework Core
Logging configuration is commonly provided by the Logging section of appsettings.{Environs} .json files. To log SQL statements, add "Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command": "Information" to the appsettings.Evolution.json file:
{ "ConnectionStrings": { "DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=MyDB-2;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true" }, "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Information", "Microsoft": "Warning", "Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information" ,"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command": "Data" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*" } With the preceding JSON, SQL statements are displayed on the command line and in the Visual Studio output window.
For more information, meet Logging in .NET Core and ASP.Internet Cadre and this GitHub effect.
Advance to the adjacent tutorial to learn how to perform basic Crud (create, read, update, delete) operations.
This tutorial teaches ASP.Cyberspace Core MVC and Entity Framework Cadre with controllers and views. Razor Pages is an culling programming model. For new development, nosotros recommend Razor Pages over MVC with controllers and views. See the Razor Pages version of this tutorial. Each tutorial covers some cloth the other doesn't:
Some things this MVC tutorial has that the Razor Pages tutorial doesn't:
- Implement inheritance in the data model
- Perform raw SQL queries
- Utilise dynamic LINQ to simplify lawmaking
Some things the Razor Pages tutorial has that this one doesn't:
- Utilise Select method to load related data
- All-time practices for EF.
The Contoso University sample spider web application demonstrates how to create ASP.Net Core 2.2 MVC spider web applications using Entity Framework (EF) Core 2.2 and Visual Studio 2017 or 2019.
This tutorial has not been updated for ASP.NET Core 3.one. It has been updated for ASP.Cyberspace Core v.0.
The sample application is a web site for a fictional Contoso Academy. It includes functionality such as student admission, grade creation, and instructor assignments. This is the offset in a series of tutorials that explicate how to build the Contoso University sample application from scratch.
Prerequisites
- .NET Core SDK 2.two
- Visual Studio 2019 with the following workloads:
- ASP.Net and web development workload
- .NET Core cross-platform development workload
Troubleshooting
If you run into a trouble y'all tin't resolve, you can generally notice the solution past comparing your code to the completed project. For a listing of common errors and how to solve them, come across the Troubleshooting section of the concluding tutorial in the serial. If you don't find what you need in that location, yous can postal service a question to StackOverflow.com for ASP.NET Cadre or EF Core.
Tip
This is a series of x tutorials, each of which builds on what is washed in earlier tutorials. Consider saving a copy of the project later each successful tutorial completion. And so if y'all run into bug, you can start over from the previous tutorial instead of going dorsum to the beginning of the whole serial.
Contoso University web app
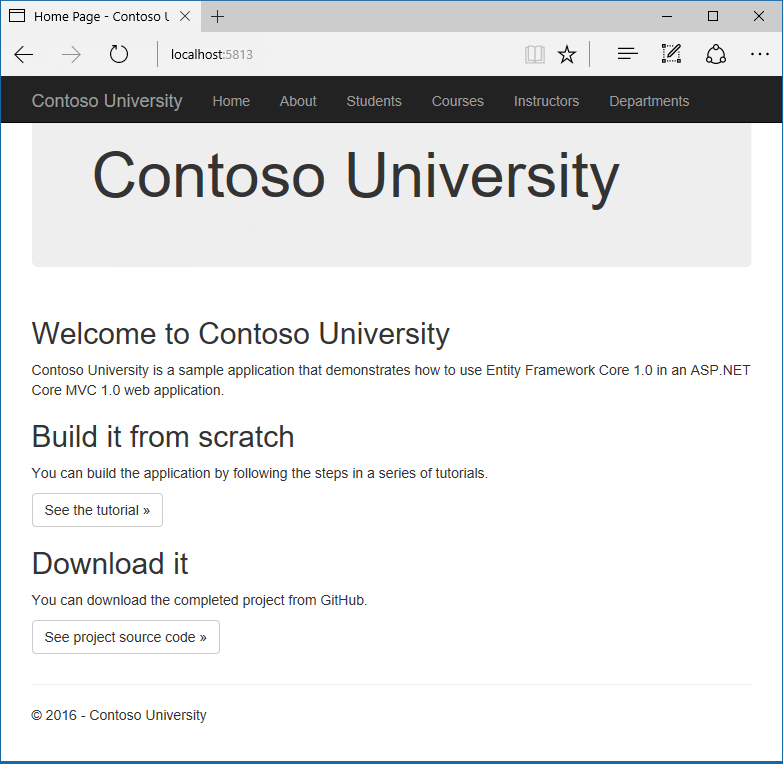
The awarding yous'll be edifice in these tutorials is a unproblematic university web site.
Users can view and update educatee, course, and instructor information. Hither are a few of the screens you'll create.


Create spider web app
-
Open Visual Studio.
-
From the File menu, select New > Project.
-
From the left pane, select Installed > Visual C# > Spider web.
-
Select the ASP.NET Core Web Application project template.
-
Enter ContosoUniversity as the name and click OK.

-
Look for the New ASP.Cyberspace Core Web Application dialog to appear.
-
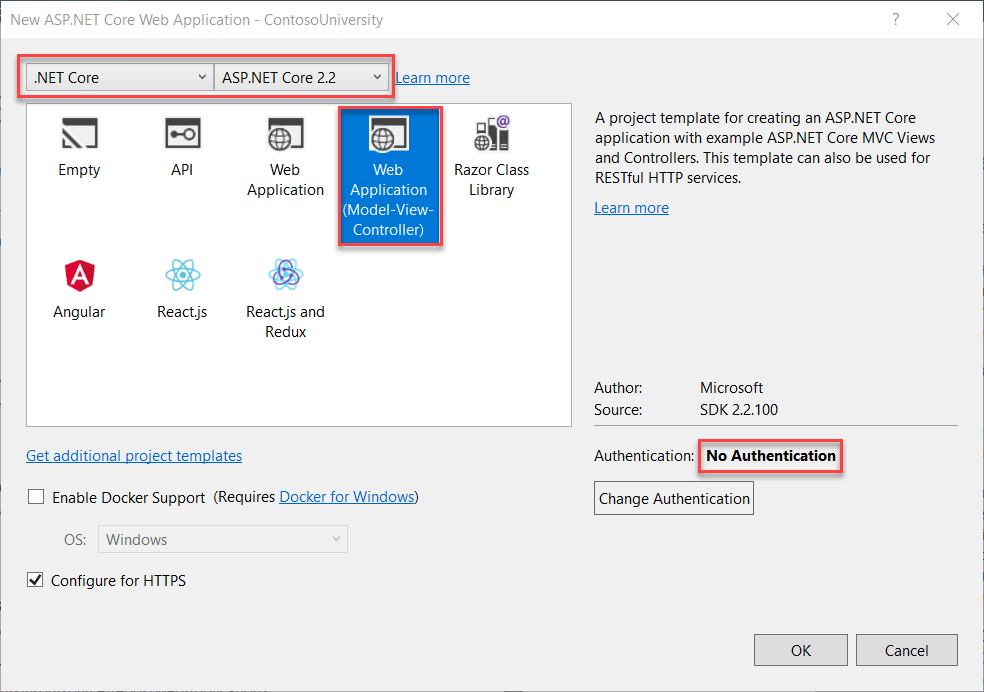
Select .NET Core, ASP.Internet Core 2.2 and the Web Application (Model-View-Controller) template.
-
Make sure Authentication is gear up to No Authentication.
-
Select OK
Prepare the site style
A few unproblematic changes will set up the site menu, layout, and home page.
Open Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml and brand the post-obit changes:
-
Change each occurrence of "ContosoUniversity" to "Contoso University". There are three occurrences.
-
Add bill of fare entries for Near, Students, Courses, Instructors, and Departments, and delete the Privacy bill of fare entry.
The changes are highlighted.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <championship>@ViewData["Championship"] - Contoso Academy</title> <surround include="Development"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css" /> </environment> <environment exclude="Development"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" asp-fallback-href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" asp-fallback-examination-class="sr-only" asp-fallback-test-property="position" asp-fallback-test-value="absolute" crossorigin="anonymous" integrity="sha256-eSi1q2PG6J7g7ib17yAaWMcrr5GrtohYChqibrV7PBE="/> </surroundings> <link rel="stylesheet" href="~/css/site.css" /> </head> <torso> <header> <nav class="navbar navbar-expand-sm navbar-toggleable-sm navbar-calorie-free bg-white border-lesser box-shadow mb-iii"> <div class="container"> <a class="navbar-make" asp-surface area="" asp-controller="Dwelling house" asp-activity="Index">Contoso University</a> <push class="navbar-toggler" blazon="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target=".navbar-plummet" aria-controls="navbarSupportedContent" aria-expanded="faux" aria-label="Toggle navigation"> <span course="navbar-toggler-icon"></bridge> </button> <div course="navbar-collapse collapse d-sm-inline-flex flex-sm-row-reverse"> <ul class="navbar-nav flex-abound-1"> <li course="nav-particular"> <a class="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Domicile" asp-action="Index">Habitation</a> </li> <li class="nav-item"> <a grade="nav-link text-dark" asp-expanse="" asp-controller="Home" asp-activity="About">About</a> </li> <li class="nav-item"> <a course="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Students" asp-activeness="Index">Students</a> </li> <li class="nav-item"> <a course="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Courses" asp-action="Index">Courses</a> </li> <li form="nav-item"> <a grade="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Instructors" asp-action="Index">Instructors</a> </li> <li form="nav-item"> <a course="nav-link text-nighttime" asp-expanse="" asp-controller="Departments" asp-activeness="Index">Departments</a> </li> </ul> </div> </div> </nav> </header> <div course="container"> <fractional name="_CookieConsentPartial" /> <main role="principal" class="pb-3"> @RenderBody() </main> </div> <footer grade="edge-peak footer text-muted"> <div form="container"> &re-create; 2019 - Contoso University - <a asp-surface area="" asp-controller="Habitation" asp-action="Privacy">Privacy</a> </div> </footer> <surroundings include="Development"> <script src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.js"></script> <script src="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.parcel.js"></script> </environment> <environment exclude="Development"> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.three.ane/jquery.min.js" asp-fallback-src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js" asp-fallback-exam="window.jQuery" crossorigin="anonymous" integrity="sha256-FgpCb/KJQlLNfOu91ta32o/NMZxltwRo8QtmkMRdAu8="> </script> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/4.one.3/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js" asp-fallback-src="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.package.min.js" asp-fallback-exam="window.jQuery && window.jQuery.fn && window.jQuery.fn.modal" crossorigin="anonymous" integrity="sha256-Eastward/V4cWE4qvAeO5MOhjtGtqDzPndRO1LBk8lJ/PR7CA4="> </script> </environment> <script src="~/js/site.js" asp-append-version="truthful"></script> @RenderSection("Scripts", required: simulated) </body> </html> In Views/Home/Index.cshtml, supercede the contents of the file with the following code to replace the text near ASP.NET and MVC with text about this awarding:
@{ ViewData["Championship"] = "Home Page"; } <div class="jumbotron"> <h1>Contoso University</h1> </div> <div course="row"> <div course="col-doctor-iv"> <h2>Welcome to Contoso University</h2> <p> Contoso University is a sample awarding that demonstrates how to utilise Entity Framework Core in an ASP.Cyberspace Cadre MVC web application. </p> </div> <div class="col-md-4"> <h2>Build it from scratch</h2> <p>You tin can build the awarding by following the steps in a serial of tutorials.</p> <p><a grade="btn btn-default" href="https://docs.asp.net/en/latest/data/ef-mvc/intro.html">See the tutorial »</a></p> </div> <div class="col-md-4"> <h2>Download it</h2> <p>You can download the completed project from GitHub.</p> <p><a grade="btn btn-default" href="https://github.com/dotnet/AspNetCore.Docs/tree/principal/aspnetcore/data/ef-mvc/intro/samples/cu-final">Run across project source code »</a></p> </div> </div> Press CTRL+F5 to run the projection or choose Debug > Commencement Without Debugging from the carte. You run into the home page with tabs for the pages you'll create in these tutorials.
Virtually EF Core NuGet packages
To add EF Core support to a projection, install the database provider that you want to target. This tutorial uses SQL Server, and the provider packet is Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer. This parcel is included in the Microsoft.AspNetCore.App metapackage, so you lot don't need to reference the package.
The EF SQL Server packet and its dependencies (Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore and Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Relational) provide runtime back up for EF. You'll add a tooling package later, in the Migrations tutorial.
For information about other database providers that are available for Entity Framework Cadre, run into Database providers.
Create the data model
Adjacent you'll create entity classes for the Contoso University application. Yous'll first with the post-obit three entities.

There'south a ane-to-many relationship between Student and Enrollment entities, and at that place's a 1-to-many relationship between Course and Enrollment entities. In other words, a pupil can be enrolled in any number of courses, and a course tin can accept whatsoever number of students enrolled in it.
In the following sections yous'll create a class for each one of these entities.
The Student entity

In the Models binder, create a class file named Student.cs and replace the template lawmaking with the following lawmaking.
using Organisation; using System.Collections.Generic; namespace ContosoUniversity.Models { public class Student { public int ID { get; gear up; } public cord LastName { go; set; } public string FirstMidName { get; set; } public DateTime EnrollmentDate { get; set; } public ICollection<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set up; } } } The ID property will become the primary key cavalcade of the database table that corresponds to this grade. By default, the Entity Framework interprets a property that's named ID or classnameID as the chief key.
The Enrollments property is a navigation belongings. Navigation properties concur other entities that are related to this entity. In this case, the Enrollments property of a Student entity will concord all of the Enrollment entities that are related to that Student entity. In other words, if a Educatee row in the database has ii related Enrollment rows (rows that contain that student'due south master key value in their StudentID foreign central cavalcade), that Pupil entity'southward Enrollments navigation holding will contain those ii Enrollment entities.
If a navigation property tin can hold multiple entities (equally in many-to-many or one-to-many relationships), its blazon must exist a list in which entries can be added, deleted, and updated, such as ICollection<T>. You can specify ICollection<T> or a type such as Listing<T> or HashSet<T>. If you lot specify ICollection<T>, EF creates a HashSet<T> collection by default.
The Enrollment entity

In the Models folder, create Enrollment.cs and supersede the existing code with the following code:
namespace ContosoUniversity.Models { public enum Grade { A, B, C, D, F } public class Enrollment { public int EnrollmentID { get; set; } public int CourseID { get; set; } public int StudentID { go; gear up; } public Form? Grade { get; set; } public Course Course { get; set; } public Educatee Educatee { become; set up; } } } The EnrollmentID property will be the chief cardinal; this entity uses the classnameID pattern instead of ID by itself as y'all saw in the Pupil entity. Usually you would choose i pattern and use it throughout your information model. Here, the variation illustrates that you tin use either blueprint. In a later tutorial, you'll see how using ID without classname makes it easier to implement inheritance in the data model.
The Grade property is an enum. The question mark subsequently the Grade type declaration indicates that the Grade belongings is nullable. A grade that'southward null is different from a zero grade -- zilch ways a grade isn't known or hasn't been assigned all the same.
The StudentID property is a foreign key, and the corresponding navigation holding is Pupil. An Enrollment entity is associated with i Student entity, so the property tin can only hold a unmarried Educatee entity (unlike the Pupil.Enrollments navigation holding you saw earlier, which can hold multiple Enrollment entities).
The CourseID property is a strange key, and the corresponding navigation holding is Form. An Enrollment entity is associated with i Course entity.
Entity Framework interprets a belongings equally a foreign key property if it's named <navigation belongings proper name><main key property name> (for example, StudentID for the Student navigation property since the Student entity'southward primary fundamental is ID). Foreign key backdrop tin can also be named simply <primary fundamental property name> (for example, CourseID since the Course entity's primary key is CourseID).
The Class entity

In the Models folder, create Class.cs and supersede the existing lawmaking with the post-obit code:
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; namespace ContosoUniversity.Models { public form Course { [DatabaseGenerated(DatabaseGeneratedOption.None)] public int CourseID { get; set up; } public string Title { get; set; } public int Credits { get; set; } public ICollection<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } } } The Enrollments holding is a navigation property. A Course entity can be related to whatever number of Enrollment entities.
We'll say more about the DatabaseGenerated attribute in a later tutorial in this series. Basically, this attribute lets you enter the primary key for the form rather than having the database generate it.
Create the database context
The main class that coordinates Entity Framework functionality for a given data model is the database context class. Yous create this class past deriving from the Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.DbContext class. In your code yous specify which entities are included in the data model. You can also customize sure Entity Framework beliefs. In this project, the class is named SchoolContext.
In the projection binder, create a folder named Information.
In the Data binder create a new grade file named SchoolContext.cs, and supplant the template code with the following code:
using ContosoUniversity.Models; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; namespace ContosoUniversity.Information { public form SchoolContext : DbContext { public SchoolContext(DbContextOptions<SchoolContext> options) : base(options) { } public DbSet<Form> Courses { get; fix; } public DbSet<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } } } This code creates a DbSet belongings for each entity set. In Entity Framework terminology, an entity set typically corresponds to a database table, and an entity corresponds to a row in the tabular array.
You lot could've omitted the DbSet<Enrollment> and DbSet<Grade> statements and it would piece of work the aforementioned. The Entity Framework would include them implicitly because the Pupil entity references the Enrollment entity and the Enrollment entity references the Course entity.
When the database is created, EF creates tables that have names the same every bit the DbSet property names. Property names for collections are typically plural (Students rather than Student), just developers disagree about whether table names should be pluralized or not. For these tutorials you'll override the default behavior by specifying singular table names in the DbContext. To practise that, add together the post-obit highlighted code after the final DbSet property.
using ContosoUniversity.Models; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; namespace ContosoUniversity.Information { public form SchoolContext : DbContext { public SchoolContext(DbContextOptions<SchoolContext> options) : base(options) { } public DbSet<Course> Courses { go; set; } public DbSet<Enrollment> Enrollments { get; set; } public DbSet<Student> Students { get; fix; } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Course>().ToTable("Form"); modelBuilder.Entity<Enrollment>().ToTable("Enrollment"); modelBuilder.Entity<Student>().ToTable("Educatee"); } } } Build the projection as a check for compiler errors.
Register the SchoolContext
ASP.NET Core implements dependency injection by default. Services (such equally the EF database context) are registered with dependency injection during application startup. Components that require these services (such as MVC controllers) are provided these services via constructor parameters. You'll see the controller constructor code that gets a context instance later in this tutorial.
To register SchoolContext every bit a service, open Startup.cs, and add the highlighted lines to the ConfigureServices method.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.Configure<CookiePolicyOptions>(options => { options.CheckConsentNeeded = context => true; options.MinimumSameSitePolicy = SameSiteMode.None; }); services.AddDbContext<SchoolContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"))); services.AddMvc(); } The proper noun of the connection string is passed in to the context past calling a method on a DbContextOptionsBuilder object. For local evolution, the ASP.Internet Core configuration system reads the connexion string from the appsettings.json file.
Add using statements for ContosoUniversity.Data and Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore namespaces, and then build the project.
using ContosoUniversity.Data; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; Open the appsettings.json file and add a connection string as shown in the following example.
{ "ConnectionStrings": { "DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Database=ContosoUniversity1;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true" }, "Logging": { "IncludeScopes": false, "LogLevel": { "Default": "Warning" } } } SQL Server Express LocalDB
The connection string specifies a SQL Server LocalDB database. LocalDB is a lightweight version of the SQL Server Express Database Engine and is intended for application development, not production use. LocalDB starts on demand and runs in user mode, so there'due south no complex configuration. By default, LocalDB creates .mdf database files in the C:/Users/<user> directory.
Initialize DB with test information
The Entity Framework will create an empty database for you. In this department, you write a method that'southward called after the database is created in order to populate it with examination information.
Here yous'll use the EnsureCreated method to automatically create the database. In a later tutorial yous'll run into how to handle model changes by using Code First Migrations to modify the database schema instead of dropping and re-creating the database.
In the Data folder, create a new form file named DbInitializer.cs and replace the template code with the following lawmaking, which causes a database to be created when needed and loads examination data into the new database.
using ContosoUniversity.Models; using System; using Arrangement.Linq; namespace ContosoUniversity.Data { public static class DbInitializer { public static void Initialize(SchoolContext context) { context.Database.EnsureCreated(); // Expect for whatsoever students. if (context.Students.Any()) { return; // DB has been seeded } var students = new Student[] { new Educatee{FirstMidName="Carson",LastName="Alexander",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2005-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Meredith",LastName="Alonso",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Arturo",LastName="Anand",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2003-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Gytis",LastName="Barzdukas",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Yan",LastName="Li",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2002-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Peggy",LastName="Justice",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2001-09-01")}, new Pupil{FirstMidName="Laura",LastName="Norman",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2003-09-01")}, new Student{FirstMidName="Nino",LastName="Olivetto",EnrollmentDate=DateTime.Parse("2005-09-01")} }; foreach (Student s in students) { context.Students.Add(s); } context.SaveChanges(); var courses = new Course[] { new Form{CourseID=1050,Title="Chemistry",Credits=3}, new Grade{CourseID=4022,Title="Microeconomics",Credits=three}, new Course{CourseID=4041,Title="Macroeconomics",Credits=three}, new Course{CourseID=1045,Championship="Calculus",Credits=4}, new Course{CourseID=3141,Title="Trigonometry",Credits=iv}, new Form{CourseID=2021,Title="Composition",Credits=3}, new Course{CourseID=2042,Title="Literature",Credits=iv} }; foreach (Course c in courses) { context.Courses.Add(c); } context.SaveChanges(); var enrollments = new Enrollment[] { new Enrollment{StudentID=i,CourseID=1050,Grade=Grade.A}, new Enrollment{StudentID=1,CourseID=4022,Grade=Form.C}, new Enrollment{StudentID=i,CourseID=4041,Grade=Grade.B}, new Enrollment{StudentID=2,CourseID=1045,Class=Grade.B}, new Enrollment{StudentID=two,CourseID=3141,Grade=Grade.F}, new Enrollment{StudentID=2,CourseID=2021,Course=Form.F}, new Enrollment{StudentID=3,CourseID=1050}, new Enrollment{StudentID=4,CourseID=1050}, new Enrollment{StudentID=4,CourseID=4022,Grade=Grade.F}, new Enrollment{StudentID=5,CourseID=4041,Class=Grade.C}, new Enrollment{StudentID=half dozen,CourseID=1045}, new Enrollment{StudentID=seven,CourseID=3141,Grade=Grade.A}, }; foreach (Enrollment e in enrollments) { context.Enrollments.Add(e); } context.SaveChanges(); } } } The code checks if in that location are any students in the database, and if not, it assumes the database is new and needs to be seeded with test information. It loads test data into arrays rather than List<T> collections to optimize performance.
In Program.cs, alter the Main method to practice the following on application startup:
- Get a database context example from the dependency injection container.
- Phone call the seed method, passing to it the context.
- Dispose the context when the seed method is washed.
using ContosoUniversity.Data; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using Organisation; namespace ContosoUniversity { public class Program { public static void Principal(cord[] args) { var host = CreateHostBuilder(args).Build(); CreateDbIfNotExists(host); host.Run(); } individual static void CreateDbIfNotExists(IHost host) { using (var scope = host.Services.CreateScope()) { var services = scope.ServiceProvider; endeavor { var context = services.GetRequiredService<SchoolContext>(); DbInitializer.Initialize(context); } catch (Exception ex) { var logger = services.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Plan>>(); logger.LogError(ex, "An fault occurred creating the DB."); } } } public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(cord[] args) => Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) .ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder => { webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>(); }); } } The first time you run the awarding, the database will exist created and seeded with exam data. Whenever you change the data model:
- Delete the database.
- Update the seed method, and offset afresh with a new database the aforementioned style.
In later tutorials, you lot'll see how to modify the database when the data model changes, without deleting and re-creating it.
Create controller and views
In this department, the scaffolding engine in Visual Studio is used to add together an MVC controller and views that will use EF to query and salve data.
The automatic creation of Crud action methods and views is known as scaffolding. Scaffolding differs from code generation in that the scaffolded code is a starting point that you can change to suit your own requirements, whereas you typically don't modify generated lawmaking. When you lot need to customize generated code, y'all employ fractional classes or you regenerate the code when things change.
- Right-click the Controllers binder in Solution Explorer and select Add > New Scaffolded Item.
- In the Add Scaffold dialog box:
- Select MVC controller with views, using Entity Framework.
- Click Add. The Add together MVC Controller with views, using Entity Framework dialog box appears:

- In Model course select Student.
- In Data context class select SchoolContext.
- Accept the default StudentsController as the proper name.
- Click Add together.
The Visual Studio scaffolding engine creates a StudentsController.cs file and a set of views (.cshtml files) that piece of work with the controller.
Notice the controller takes a SchoolContext as a constructor parameter.
namespace ContosoUniversity.Controllers { public course StudentsController : Controller { private readonly SchoolContext _context; public StudentsController(SchoolContext context) { _context = context; } ASP.NET Core dependency injection takes care of passing an instance of SchoolContext into the controller. That was configured in the Startup.cs file.
The controller contains an Index activeness method, which displays all students in the database. The method gets a list of students from the Students entity set by reading the Students property of the database context example:
public async Task<IActionResult> Alphabetize() { return View(await _context.Students.ToListAsync()); } You acquire about the asynchronous programming elements in this code later in the tutorial.
The Views/Students/Index.cshtml view displays this list in a tabular array:
@model IEnumerable<ContosoUniversity.Models.Educatee> @{ ViewData["Title"] = "Index"; } <h2>Index</h2> <p> <a asp-activeness="Create">Create New</a> </p> <table course="table"> <thead> <tr> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.LastName) </th> <thursday> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.FirstMidName) </th> <thursday> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.EnrollmentDate) </thursday> <th></th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> @foreach (var item in Model) { <tr> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => particular.LastName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FirstMidName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => detail.EnrollmentDate) </td> <td> <a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Edit</a> | <a asp-activeness="Details" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Details</a> | <a asp-action="Delete" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Delete</a> </td> </tr> } </tbody> </table> Printing CTRL+F5 to run the projection or choose Debug > Start Without Debugging from the carte.
Click the Students tab to see the test information that the DbInitializer.Initialize method inserted. Depending on how narrow your browser window is, yous'll come across the Students tab link at the tiptop of the page or yous'll have to click the navigation icon in the upper right corner to see the link.


View the database
When you lot started the application, the DbInitializer.Initialize method calls EnsureCreated. EF saw that at that place was no database and so information technology created one, then the remainder of the Initialize method code populated the database with data. You tin can utilize SQL Server Object Explorer (SSOX) to view the database in Visual Studio.
Close the browser.
If the SSOX window isn't already open, select it from the View menu in Visual Studio.
In SSOX, click (localdb)\MSSQLLocalDB > Databases, and and then click the entry for the database name that'southward in the connectedness cord in the appsettings.json file.
Expand the Tables node to see the tables in the database.

Right-click the Student tabular array and click View Information to see the columns that were created and the rows that were inserted into the table.

The .mdf and .ldf database files are in the C:\Users\<username> folder.
Because you're calling EnsureCreated in the initializer method that runs on app start, you could now make a change to the Student class, delete the database, run the application once again, and the database would automatically be re-created to lucifer your alter. For instance, if you lot add an EmailAddress property to the Educatee class, you'll see a new EmailAddress column in the re-created tabular array.
Conventions
The amount of code you had to write in gild for the Entity Framework to be able to create a complete database for yous is minimal because of the use of conventions, or assumptions that the Entity Framework makes.
- The names of
DbSetbackdrop are used equally table names. For entities not referenced by aDbSetproperty, entity class names are used as tabular array names. - Entity holding names are used for cavalcade names.
- Entity backdrop that are named ID or classnameID are recognized as chief key properties.
- A property is interpreted as a foreign key holding if information technology's named <navigation property proper noun><primary key property name> (for example,
StudentIDfor thePupilnavigation property since theEducateeentity's primary central isID). Foreign key properties can also be named simply <master cardinal property name> (for example,EnrollmentIDsince theEnrollmententity's principal key isEnrollmentID).
Conventional beliefs can be overridden. For example, you can explicitly specify tabular array names, as you lot saw earlier in this tutorial. And yous can set cavalcade names and set up any property as master primal or foreign central, every bit you'll encounter in a later tutorial in this serial.
Asynchronous lawmaking
Asynchronous programming is the default mode for ASP.NET Core and EF Core.
A web server has a limited number of threads bachelor, and in high load situations all of the bachelor threads might exist in utilize. When that happens, the server can't process new requests until the threads are freed upwards. With synchronous code, many threads may exist tied up while they aren't actually doing any work because they're waiting for I/O to complete. With asynchronous code, when a procedure is waiting for I/O to complete, its thread is freed upward for the server to use for processing other requests. As a result, asynchronous lawmaking enables server resources to be used more than efficiently, and the server is enabled to handle more than traffic without delays.
Asynchronous code does innovate a small amount of overhead at run fourth dimension, but for low traffic situations the performance striking is negligible, while for high traffic situations, the potential performance improvement is substantial.
In the following lawmaking, the async keyword, Task<T> return value, await keyword, and ToListAsync method make the code execute asynchronously.
public async Chore<IActionResult> Index() { render View(expect _context.Students.ToListAsync()); } - The
asynckeyword tells the compiler to generate callbacks for parts of the method body and to automatically create theTask<IActionResult>object that'due south returned. - The return blazon
Task<IActionResult>represents ongoing work with a result of typeIActionResult. - The
awaitkeyword causes the compiler to split the method into 2 parts. The first part ends with the functioning that'due south started asynchronously. The 2d part is put into a callback method that's called when the functioning completes. -
ToListAsyncis the asynchronous version of theToListextension method.
Some things to be aware of when you are writing asynchronous code that uses the Entity Framework:
- Simply statements that crusade queries or commands to be sent to the database are executed asynchronously. That includes, for example,
ToListAsync,SingleOrDefaultAsync, andSaveChangesAsync. It doesn't include, for case, statements that simply change anIQueryable, such asvar students = context.Students.Where(southward => s.LastName == "Davolio"). - An EF context isn't thread prophylactic: don't try to do multiple operations in parallel. When y'all call whatever async EF method, always use the
expectkeyword. - If y'all desire to take advantage of the performance benefits of async code, make certain that whatsoever library packages that you're using (such as for paging), as well use async if they phone call whatever Entity Framework methods that cause queries to be sent to the database.
For more information near asynchronous programming in .Net, come across Async Overview.
Adjacent steps
Advance to the next tutorial to learn how to perform basic CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations.
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/data/ef-mvc/intro
0 Response to "How to Run Database Initializer Again"
Post a Comment